Consuming an abundance of potassium present in many foods naturally, can help reduce blood pressure by opposing the damaging effects of sodium. This is due to the fact that an excess of sodium makes the body retain water, which puts more pressure on the walls of blood vessels. However, you excrete more sodium when you eat meals high in potassium. Due to its ability to dilate, or expand, blood vessels and facilitate smoother blood flow, potassium can also contribute to lowering blood pressure. (Filippini et al., 2020)
Your Diet And Potassium
For a typical adult aged 19 to 50, the recommended daily consumption of potassium is 2,600 mg for females and around 3,400 mg for males.
Numerous components of the DASH (Dietary Strategies to Stop Hypertension) diet, such as fish, vegetables, dairy products with minimal or no fat, and fruits, are excellent organic sources of potassium. For instance, half a cup of simple mashed sweet potato has 456 mg of potassium, whereas a medium banana contains around 226 mg. (Staruschenko, 2018)
Mechanism Of Action Of Potassium In BP Regulation
The most prevalent intracellular ion is potassium, which has a well-established function in controlling blood pressure. Potassium supplements to the diet can reduce blood pressure in both hypertensive and normal persons. Potassium channels play a crucial role in regulating the resting potential of the membrane and cell volume, as does Na+-K+-ATPase, commonly referred to as the Na+-K+ pump.
Since intracellular medium contains a significantly greater concentration of potassium than external media, activation and subsequent opening of the potassium channel causes the plasma membrane to become hyperpolarized, which modifies the electrogenic driving force of Na+ reabsorption within the distal nephron. (Publishing, 2017)
The amount of fluid your body stores and excretes in your urine is influenced by potassium. Your blood will contain more fluid if the body is retaining water. This increases the pressure exerted on the walls of the arteries, so raising the pressure in your blood.
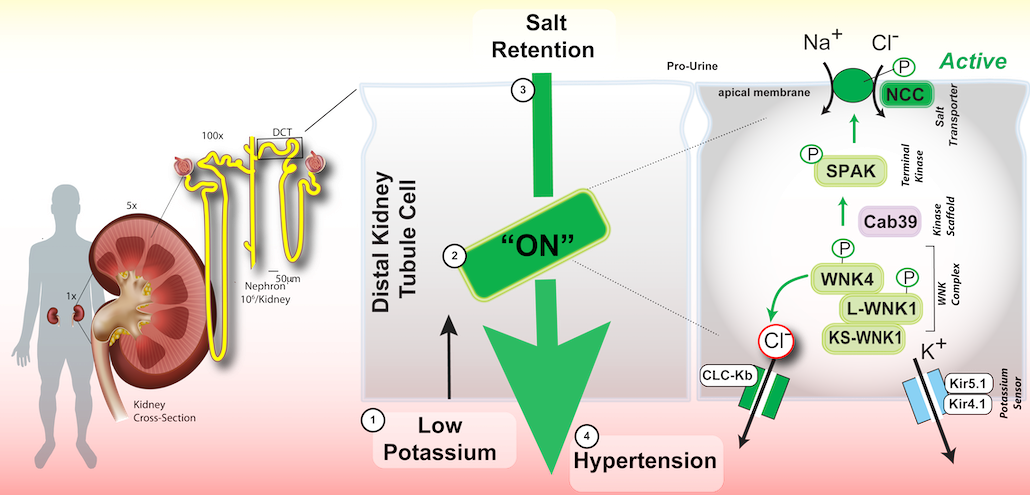
Normally, the kidneys filter extra fluid into the bladder after removing it from the blood. A precise sodium and potassium balance is required for this procedure. The component of salt that raises blood pressure is sodium. Your blood will have more sodium if you consume too much salt, and sodium retains water.
This throws off the delicate sodium and potassium balance required for the kidneys to draw water from the blood. Increased consumption of potassium-rich foods can aid in reestablishing equilibrium, promoting healthy kidney function and lowering blood pressure. (Staruschenko, 2018)
Which Foods Have The Highest Potassium Content?
Potassium is abundant in many fresh produce, as well as in nuts, legumes, and seafood. Here are a few instances of potassium content per serving, listed in decreasing order: (Courtney, 2023)
Baked potato | 941 mg |
Lentils | 1 cup: 731 mg |
Plain yogurt | 1 cup: 579 mg |
Baked sweet potato | 542 mg |
Halibut | 3 oz: 449 mg |
Banana | 422 mg |
Cooked spinach | ½ cup: 419 mg |
Carrots | 1 cup: 410 mg |
Dried apricots | ¼ cup: 378 mg |
Pinto beans | ½ cup: 373 mg |
Avocado | ½ cup: 364 mg |
Broccoli | 1 cup: 288 mg |
Orange | 237 mg |
Almonds | 1 ounce: 200 mg |
Grapes | 1 cup: 176 mg |
Walnuts | 1 ounce: 125 mg |
Effect Of Potassium Supplements and Pills
People with high blood pressure who took an everyday potassium supplement saw an average decrease in the systolic pressure of almost 4.5 mm Hg and their diastolic pressure of around 3 mm Hg, according to a review of 25 clinical trials published in the European Journal of Cardiology. Over the course of four to fifteen weeks, the trial participants consumed between 1,200 mg to 4,700 mg potassium daily. (Publishing, 2017)
Potassium supplements should not be taken by those who have renal illness or hyperkalemia, a condition in which there is an excess of potassium in the blood.
Diuretics, or water tablets, can remove too much potassium from the urine, which is typically the cause of low potassium levels. Because diuretics aid in the body's salt elimination, they may be recommended as a therapy for high blood pressure. (Courtney, 2023)
Overdose Of Potassium
As crucial as k is for preserving a normal blood pressure, an excess of it might result in severe heart failure or an erratic pulse. Potassium overdose symptoms might include dizziness, nausea, and a weak, erratic pulse. (Filippini et al., 2020)
Conclusion
Since potassium reduces the sodium effects therefore foods that are rich in potassium are useful for treating high blood pressure. You lose more salt through urine based on how much potassium you consume. Additionally, potassium dilates the blood vessels walls, which reduces blood pressure even more.
References:
1. Filippini, T., Naska, A., Kasdagli, M., Torres, D., Lopes, C., Carvalho, C., Moreira, P., Malavolti, M., Orsini, N., Whelton, P. K., & Vinceti, M. (2020). Potassium intake and blood pressure: A dose‐response meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of the American Heart Association, 9(12). https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.119.015719
2. Staruschenko, A. (2018). Beneficial Effects of High Potassium. Hypertension, 71(6), 1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.118.10267
3. Publishing, H. H. (2017, January 23). Potassium lowers blood pressure. Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/potassium-lowers-blood-pressure
4. Courtney Perkes. (2 May, 2023) How Potassium and Blood Pressure Are Related. https://www.healthcentral.com/article/sudden-dramatic-increased-blood-pressure
WRITTEN BY Checkme
Related Blogs
Recommended Products
Subscribe for special promotions,
healthy knowledge, and more!





